Sarah Anderson
CEOs of major U.S. military contractors stand to reap huge windfalls from the escalation of conflict with Iran. This was evident in the immediate aftermath of the U.S. assassination of a top Iranian military official last week. As soon as the news reached financial markets, these companies’ share prices spiked, inflating the value of their executives’ stock-based pay.
I took a look at how the CEOs at the top five Pentagon contractors were affected by this surge, using the most recent SEC information on their stock holdings.
Northrop Grumman executives saw the biggest increase in the value of their stocks after the U.S. airstrike that killed Qasem Suleimani on January 2. Shares in the B-2 bomber maker rose 5.43 percent by the end of trading the following day.
Wesley Bush, who turned Northrop Grumman’s reins over to Kathy Warden last year, held 251,947 shares of company stock in various trusts as of his final SEC Form 4 filing in May 2019. (Companies must submit these reports when top executives and directors buy and sell company stock.) Assuming Bush is still sitting on that stockpile, he saw the value grow by $4.9 million to a total of $94.5 million last Friday.
New Northrop Grumman CEO Warden saw the 92,894 shares she’d accumulated as the firm’s COO expand in value by more than $2.7 million in just one day of post-assassination trading.
Lockheed Martin, whose Hellfire missiles were reportedly used in the attack at the Baghdad airport, saw a 3.6 percent increase in price per share on January 3. Marillyn Hewson, CEO of the world’s largest weapon maker, may be kicking herself for selling off a considerable chunk of stock last year when it was trading at around $307. Nevertheless, by the time Lockheed shares reached $413 at the closing bell, her remaining stash had increased in value by about $646,000.
What about the manufacturer of the MQ-9 Reaper that carried the Hellfire missiles? That would be General Atomics. Despite raking in $2.8 billion in taxpayer-funded contracts in 2018, the drone maker is not required to disclose executive compensation information because it is a privately held corporation.
We do know General Atomics CEO Neal Blue is worth an estimated $4.1 billion — and he’s a major investor in oil production, a sector that also stands to profit from conflict with a major oil-producing country like Iran.
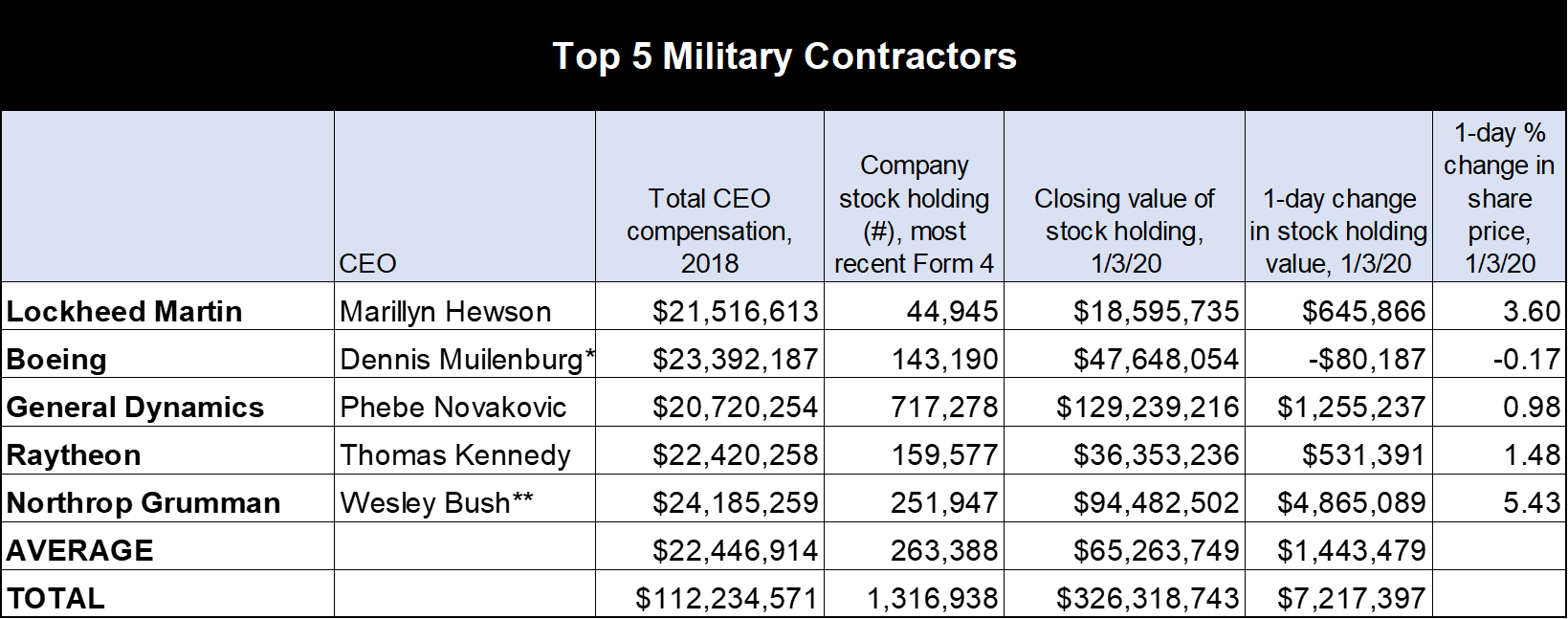
*Resigned 12/22/19. **Resigned 1/1/19 while staying on as chairman until 7/19. New CEO Kathy Warden accumulated 92,894 shares in her previous position as Northrop Grumman COO.
Suleimani’s killing also inflated the value of General Dynamics CEO Phebe Novakovic’s fortune. As the weapon maker’s share price rose about 1 percentage point on January 3, the former CIA official saw her stock holdings increase by more than $1.2 million.
Raytheon CEO Thomas Kennedy saw a single-day increase in his stock of more than half a million dollars, as the missile and bomb manufacturer’s share price increased nearly 1.5 percent. Boeing stock remained flat on Friday. But Dennis Muilenberg, recently ousted as CEO over the 737 aircraft scandal, appears to be well-positioned to benefit from any continued upward drift of the defense sector.
As of his final Form 4 report, Muilenburg was sitting on stock worth about $47.7 million. In his yet to be finalized exit package, the disgraced former executive could also pocket huge sums of currently unvested stock grants.
Hopefully sanity will soon prevail and the terrifyingly high tensions between the Trump administration and Iran will de-escalate. But even if the military stock surge of this past Friday turns out to be a market blip, it’s a sobering reminder of who stands to gain the most from a war that could put millions of lives at risk.
We can put an end to dangerous war profiteering by denying federal contracts to corporations that pay their top executives excessively. In 2008, John McCain, then a Republican presidential candidate, proposed capping CEO pay at companies receiving taxpayer bailouts at no more than $400,000 (the salary of the U.S. president). That notion should be extended to companies that receive massive taxpayer-funded contracts.
Sen. Bernie Sanders, for instance, has a plan to deny federal contracts to companies that pay CEOs more than 150 times what their typical worker makes.
As long as we allow the top executives of our privatized war economy to reap unlimited rewards, the profit motive for war in Iran — or anywhere — will persist.
No comments:
Post a Comment